AI is no longer science fiction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is an omnipresent term, but we rarely explain it with depth and clarity. Imagine we’re creating an intelligent being from scratch. This way you’ll understand how AI emerged and why it’s already part of our lives.
We’re living through a change as profound as the industrial revolution or the arrival of the internet. And the most exciting part is that this is just beginning.
🔵 1. The origin of the idea
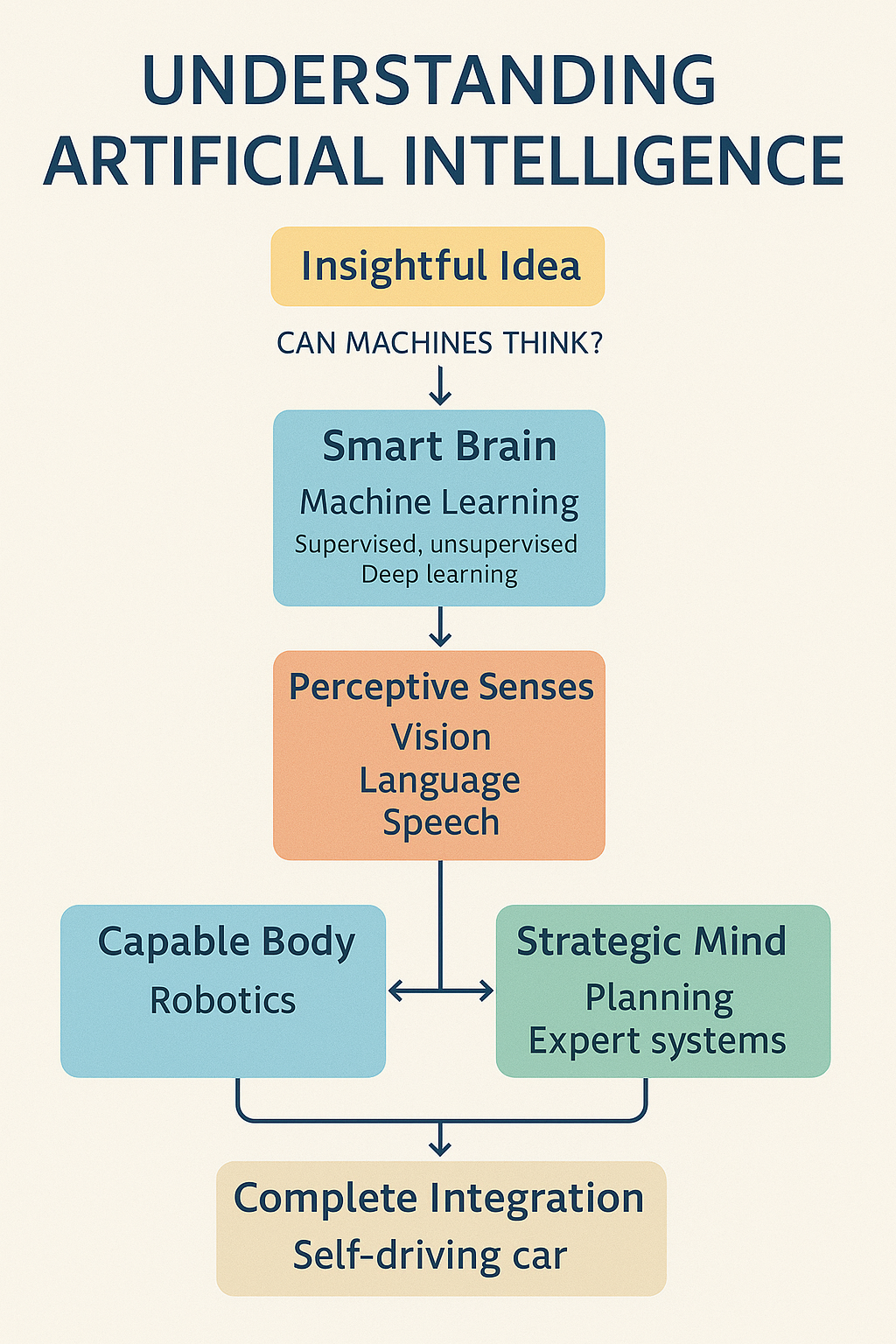
In the 1950s, visionaries like Alan Turing and John McCarthy asked themselves: Can machines think like humans? This is how AI was born, with the ambition to replicate human functions in artificial systems.
Turing proposed his famous test: if a machine can maintain a conversation indistinguishable from a human one, then it’s intelligent. McCarthy coined the term “Artificial Intelligence” at the Dartmouth Conference in 1956.
References: Alan Turing • John McCarthy
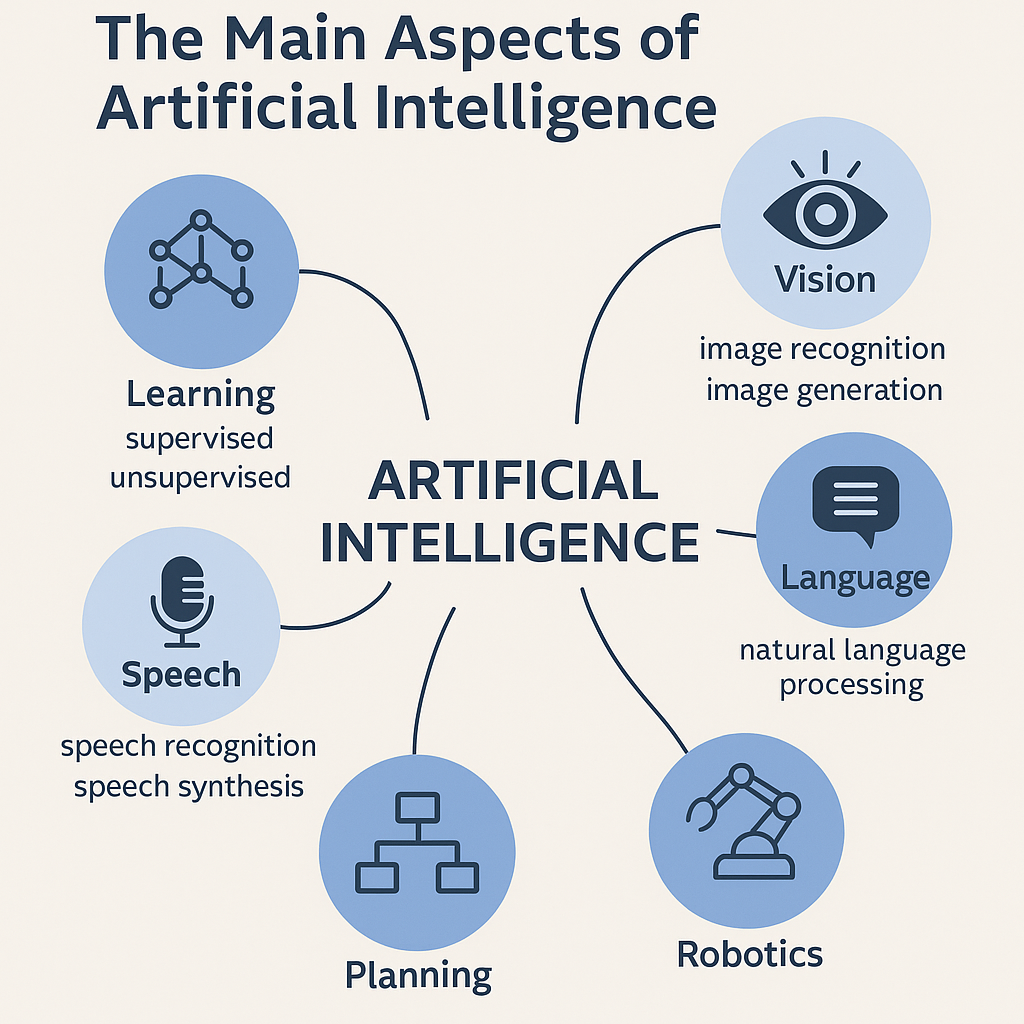
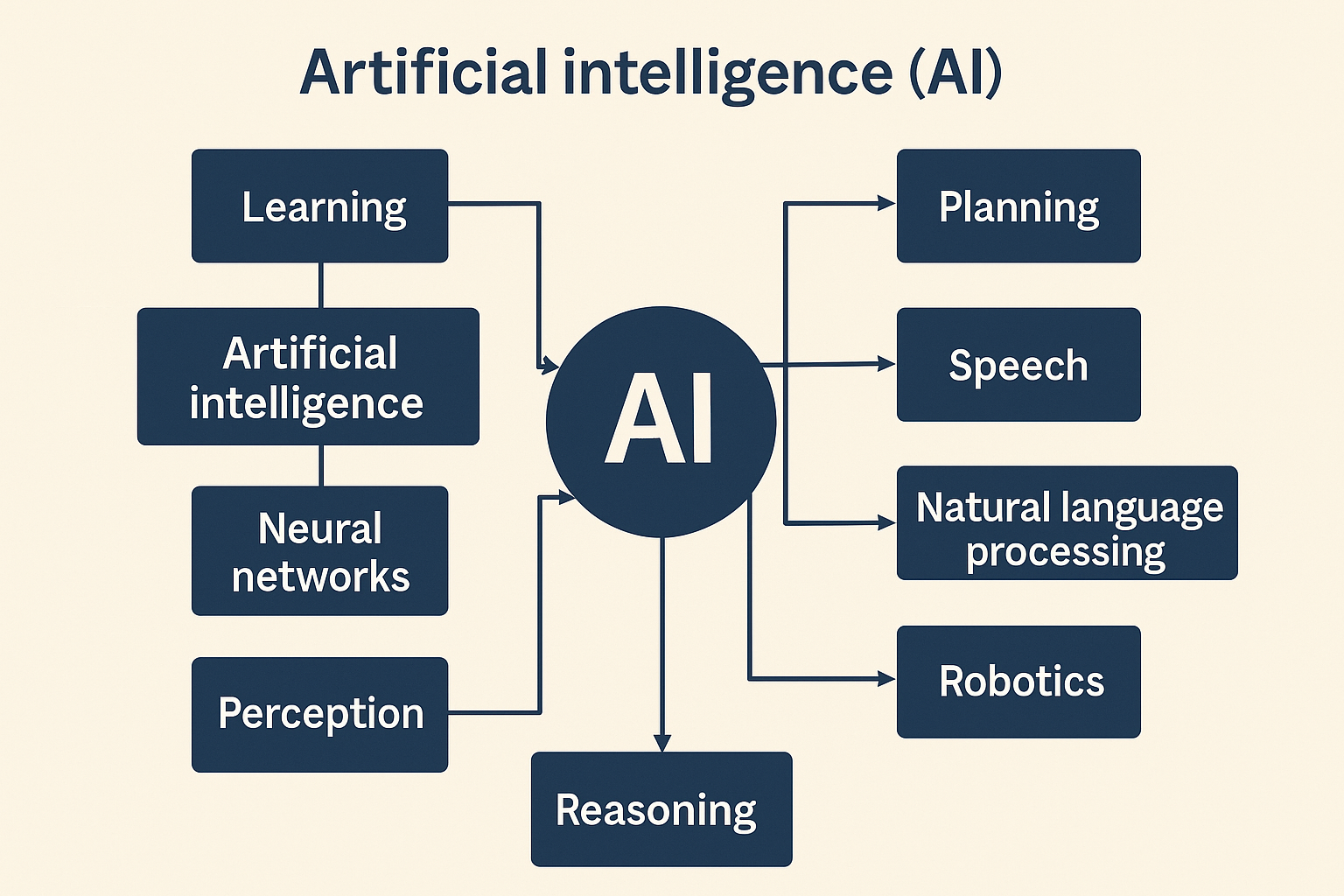
🧠 2. The brain: machine learning
For a machine to be truly “intelligent,” it must learn from experience. This is where Machine Learning (ML) comes in:
Supervised: a data “teacher” shows it examples
- Spam detection: shown thousands of emails labeled as spam or not spam
- Facial recognition: trained with millions of labeled photos
- Translation: uses pairs of phrases in different languages
Unsupervised: the model finds patterns on its own
- Customer segmentation: groups users by behavior without knowing what each group means
- Anomaly detection: identifies strange patterns in financial data
- Data compression: reduces complexity while maintaining essential information
Deep Learning: neural networks inspired by our brain
- Convolutional (CNN): recognize images with high precision
- Recurrent (RNN): process sequences like text or speech
- Transformers: revolutionized natural language processing
Technically, these models adjust thousands or millions of parameters (weights) to reduce errors during training, a process similar to human learning through trial and error.
References: Machine Learning Stanford • Deep Learning MIT
👁️ 3. The “perceptive thread”: AI senses
An intelligent being needs to perceive. AI does this too:
Computer Vision
- Facial unlock: recognizes your face in milliseconds
- Autonomous cars: detect pedestrians, signs, and obstacles
- Security cameras: identify suspicious behaviors
- Medical diagnosis: analyze X-rays and MRIs
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- Automatic translators: Google Translate, DeepL
- Chatbots: 24/7 customer service
- Text generation: ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini
- Sentiment analysis: detect emotions in social media
Speech and Voice
- Voice dictation: converts speech to text in real-time
- Automatic reading: converts text to natural speech
- Virtual assistants: Siri, Alexa, Google Assistant
- Transcription: automatically converts audio to text
Technically, these sensors use deep learning and large volumes of data to interpret the environment as a human would.
References: Computer Vision Stanford • NLP Stanford
🤖 4. The body: Robotics
With “brain” and “senses,” the body was missing. Robotics combines these elements with sensors and actuators to execute actions in the real world:
Industry
- Robotic arms: assemble products with millimeter precision
- Welding robots: work in dangerous environments
- Palletizing systems: organize products automatically
Medicine
- Surgical robots: Da Vinci performs minimally invasive operations
- Rehabilitation: exoskeletons help patients with reduced mobility
- Hospital logistics: robots transport medicines and samples
Exploration
- Explorer drones: map inaccessible terrains
- Martian rovers: Perseverance explores Mars
- Autonomous submarines: study ocean depths
Home
- Smart vacuums: Roomba maps your house
- Lawn mowers: Husqvarna maintains your garden
- Kitchen robots: Moley prepares complete meals
Technically, they integrate vision, learning, and real-time control to move with precision and adapt to the environment.
References: Robotics MIT • Da Vinci Surgery
🎯 5. The strategic mind: planning and expert systems
Acting with intelligence requires foresight and decision-making.
Planning
- Route algorithms: GPS calculates the best route considering traffic
- Logistics: optimizes delivery routes to save fuel
- Games: Deep Blue and AlphaGo plan strategic moves
- Finance: trading algorithms execute operations in microseconds
Expert Systems
- Medical diagnosis: IBM Watson suggests treatments based on symptoms
- Legal advice: analyzes cases and suggests strategies
- Engineering: optimizes bridge and building designs
- Agriculture: recommends when to water and fertilize crops
These systems combine logic, heuristics, and probabilities to make informed decisions.
References: IBM Watson • DeepMind AlphaGo
🚗 6. Complete integration: an autonomous car
An autonomous car is the perfect example of integration:
Perception
- Vision: detects pedestrians, signs, other vehicles
- Lidar: maps the environment in 3D in real-time
- Radar: measures distances and speeds
- GPS: knows its exact location
Decision
- ML: predicts behaviors of other drivers
- Planning: calculates the optimal route
- Control: decides to accelerate, brake, or turn
Action
- Actuators: controls steering, accelerator, and brakes
- Communication: connects with other vehicles
- Interface: informs you about the trip status
All this happens in milliseconds while you drive. It’s like having an expert driver who never gets distracted, never gets tired, and never makes mistakes.
References: Tesla Autopilot • Waymo
✨ 7. The new frontier: Generative AI
Today, AI doesn’t just interpret, it creates:
Text
- ChatGPT: natural and creative conversations
- Claude: professional analysis and writing
- Gemini: reasoning and problem-solving
Images
- DALL·E: creates images from descriptions
- MidJourney: high-quality digital art
- Stable Diffusion: customizable images
Multimedia
- Music: composes melodies in different styles
- Video: generates short clips and animations
- Code: writes functional programs
These models are trained with enormous amounts of data and can generate original, high-quality content that rivals human creativity.
References: OpenAI • Anthropic • Google AI
🌟 8. Final reflection: a change of era
AI already has:
- 🧠 Brain (machine learning)
- 👁️ Senses (vision, language, voice)
- 🤖 Body (robotics)
- 🎯 Strategic mind (planning and expert systems)
We’re living through a change as profound as the industrial revolution or the arrival of the internet. And the most exciting part is that this is just beginning.
“I want to be an active part of this new era, not just as a spectator but as a creator.”
🔚 Closing
Artificial Intelligence is no longer a human dream. It’s a reality that’s transforming our world. From machine learning to advanced robotics, each component works in harmony to create systems that think, perceive, and act like never before.
We’re facing a new era in human history, where the frontier between natural and artificial fades away more each day.
Recommended links:
-
The Future of AI: How AI Is Changing the World – Built In
Comprehensive analysis of how artificial intelligence is transforming various industries and our daily lives. -
The Future of AI for Robotics – 3DS Blog
Technical insights into the integration of AI and robotics for industrial and commercial applications. -
The History of AI: A Timeline of Artificial Intelligence – Coursera
Educational timeline covering the major milestones and breakthroughs in artificial intelligence development.
✍️ Claudio from ViaMind
Dare to imagine, create and transform.
